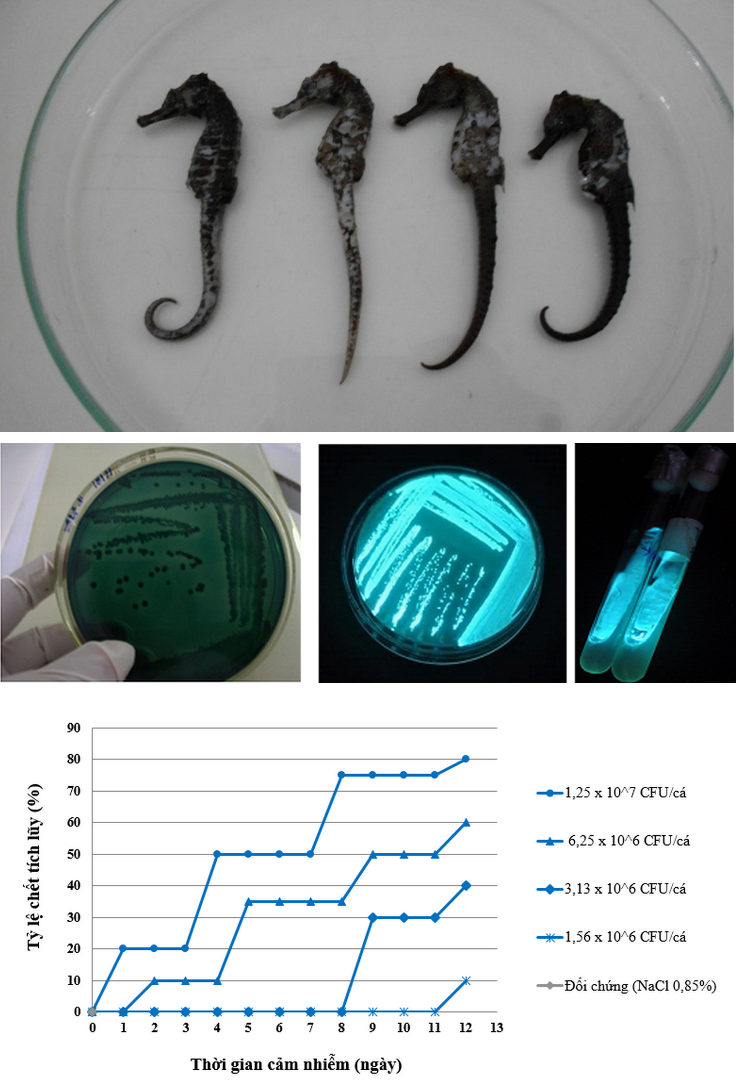
 Seahorse (Hippocampus spp.) are economically valuable species and are used in traditional medicine. In Vietnam, seahorse cultivation has been recently developed in some regions namely Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan, Hue, Da Nang and Vung Tau. Some seahorse farms in Khanh Hoa are now facing problems with unknown disease occuring in common seahorses (Hippocampus kuda Bleekers 1852). In the present study, luminous bacteria were isolated from a total of 35 Hippocampus kuda, which had ulcerations. Physiological and biochemical testing as well as 16S rDNA sequencing confirmed that the photobacterium (named TNX-X1) was closely related to Vibrio harveyi. Infectivity studies (challenge test) were conducted in Hippocampus kuda showed that this Vibrio isolate caused a disease with symptoms including white changing, viscous skin and ulceration. LD50 (Lethal dose 50%) for fish with an average body weight of 1 – 2g was 5x106 CFUxfish-1. The isolate, in addition, was resistant to certain antibiotics including ampicillin10µg/disc (A10), cefadroxil 30µg (CD30), amoxicilin 25µg (AMC25) and cefalexin 30µg (CL30) (in total 9 antibiotics).
Seahorse (Hippocampus spp.) are economically valuable species and are used in traditional medicine. In Vietnam, seahorse cultivation has been recently developed in some regions namely Khanh Hoa, Ninh Thuan, Hue, Da Nang and Vung Tau. Some seahorse farms in Khanh Hoa are now facing problems with unknown disease occuring in common seahorses (Hippocampus kuda Bleekers 1852). In the present study, luminous bacteria were isolated from a total of 35 Hippocampus kuda, which had ulcerations. Physiological and biochemical testing as well as 16S rDNA sequencing confirmed that the photobacterium (named TNX-X1) was closely related to Vibrio harveyi. Infectivity studies (challenge test) were conducted in Hippocampus kuda showed that this Vibrio isolate caused a disease with symptoms including white changing, viscous skin and ulceration. LD50 (Lethal dose 50%) for fish with an average body weight of 1 – 2g was 5x106 CFUxfish-1. The isolate, in addition, was resistant to certain antibiotics including ampicillin10µg/disc (A10), cefadroxil 30µg (CD30), amoxicilin 25µg (AMC25) and cefalexin 30µg (CL30) (in total 9 antibiotics).
Isolation, identification of luminous Vibrio in diseased cultured common seahorse (Hippocampus kuda)
Related
- Phylogeny of zoonotic parasites in fresh and brackish water fish in Vietnam (21-7-2014 12:12:31)
- Phylogenetic relationship of giant clams (Tridacna spp.) collected in the South and Central coast of Vietnam (04-8-2014 02:01:42)
- Feeding mode of cone snail (Conus spp.) and phylogenetic relationships (04-8-2014 01:59:46)
- Identification of cone snail (Conus spp.) in the coastal Central Southern Vietnam based on morophologic and gennetic chacracters (04-8-2014 01:57:34)
Others
- About us (17-7-2014 09:35:40)
- SVM30022GR0249 "Management and restoration mangrove forests in the north of Khanh Hoa province - Toward sustainable landscape" (25-10-2023 09:44:51)
- VINIF.2022.DA00021 "DNA metabarcoding and integrated information database - Implication for Ichthyoplankton survey and fisheries management in Vietnam" (25-10-2023 09:53:54)
- Riverscape Genetics to Inform Natural History of Exploited Fishes in the Lower Mekong River Basin (23-10-2017 11:43:14)
